Lithium-ion battery with silicon anode, nickel-rich cathode and in-cell sensor for electric vehicles
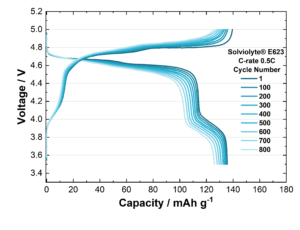
Lithium-ion batteries are the energy source of the future. Autonomy and rapid recharging are essential features to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. The EU-funded SeNSE project aims to create next-generation lithium-ion batteries with a silicon-graphite composite anode and a nickel-rich NMC cathode capable of achieving a volumetric energy density of 750 Wh/l. This new generation of batteries will also feature a sensor-based charge management system directly integrated into the cells to enable faster charging, improved durability and recyclability, and lower production costs.